🏛️ Restoration and Restoration Studies in Florence: Preserving Cultural Heritage with Precision and Passion
Florence, a city celebrated for its artistic and architectural treasures, stands as a global leader in the restoration and conservation of cultural heritage. Its commitment to safeguarding history is reflected in world-renowned restoration projects and prestigious institutions dedicated to the study of this vital craft.
🕰️ Historical Significance: A Legacy of Preservation
Florence’s role as the cradle of the Renaissance endowed it with an extraordinary collection of masterpieces. To protect these works, the city developed advanced restoration techniques that continue to evolve.
- During the Renaissance, the Medici family championed not only the creation of art but also its preservation.
- Their patronage laid the foundation for Florence’s enduring dedication to cultural conservation.
Thanks to this legacy, restoration in Florence is both a science and an art.
🧱 Major Restoration Projects: Icons Reborn
Florentine restorers have undertaken some of the most complex and celebrated projects in the world.
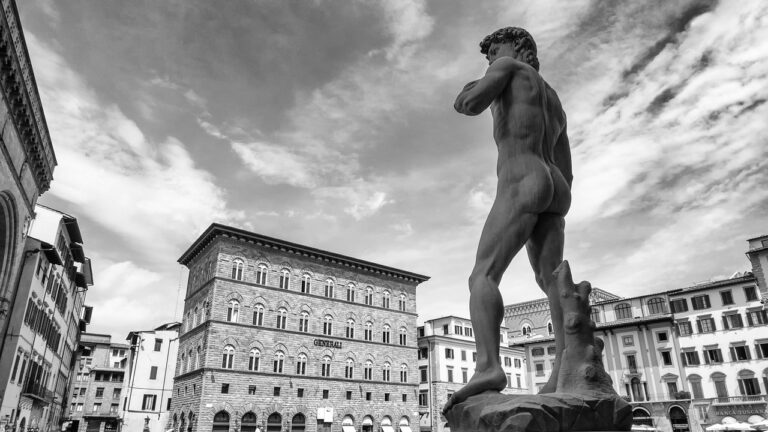
- Michelangelo’s David has undergone multiple restorations to address environmental damage and structural concerns.
- After the devastating 1966 flood, Vasari’s Last Supper was painstakingly restored over several decades, showcasing the city’s expertise and patience.
- The Gates of Paradise, Lorenzo Ghiberti’s bronze doors of the Baptistery, were meticulously cleaned and conserved to preserve their intricate beauty.
Each project reflects Florence’s unwavering commitment to preserving its cultural soul.
🏫 Renowned Restoration Institutions: Centers of Excellence
Florence is home to several prestigious institutions that lead the field in restoration and conservation.
🧪 Opificio delle Pietre Dure (OPD)
One of the world’s foremost restoration centers, OPD functions as both a museum and a research institute.
- It offers specialized training in areas such as painting, sculpture, textiles, and stone.
- The institute also conducts cutting-edge research and collaborates on international projects.
🎨 Istituto per l’Arte e il Restauro Palazzo Spinelli
This institute blends theory with practice, offering hands-on education in various restoration disciplines.
- Students work on real projects under expert guidance.
- Courses cover frescoes, ceramics, paintings, and more.
🏛️ University of Florence
Through its School of Architecture and Department of Cultural Heritage, the university provides interdisciplinary programs.
- Students study art history, science, and technology.
- The curriculum prepares them for careers in cultural preservation.
🎓 Study Programs and Courses: Learning by Doing
Florence offers a wide range of educational opportunities for aspiring restorers.
- Bachelor’s and Master’s degrees cover topics like chemistry, materials science, and restoration techniques.
- Workshops and short courses provide intensive training in specific methods or materials.
- Internships and apprenticeships allow students to gain real-world experience in museums, labs, and studios.
These programs ensure that students graduate with both knowledge and practical skills.
🔬 Restoration Techniques and Innovations: Where Science Meets Art
Modern restoration in Florence is driven by innovation and precision.
- Scientific analysis—including XRF, infrared reflectography, and spectrometry—helps identify pigments and materials.
- Non-invasive methods, such as laser cleaning, reduce the risk of damage to delicate surfaces.
- Digital tools, including 3D scanning and virtual reconstruction, aid in documentation and planning.
Together, these techniques enhance accuracy while honoring the integrity of each piece.
🧭 Cultural and Ethical Considerations: Restoring with Respect
Florentine restorers follow strict ethical guidelines to ensure authenticity and cultural sensitivity.
- Respect for originality is paramount. Restorers aim to preserve the artist’s intent without altering the work.
- Reversibility ensures that restoration efforts can be undone, allowing future experts to apply new techniques.
- Cultural sensitivity guides collaboration with institutions and communities, honoring the historical context of each artifact.
These principles safeguard both the physical and symbolic value of cultural heritage.
✨ Conclusion: Florence, Guardian of the Past
Florence’s dedication to restoration is a testament to its reverence for history and beauty. With world-class institutions, innovative techniques, and immersive study programs, the city remains a beacon for cultural preservation.
Whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply an admirer of art, Florence offers countless opportunities to explore the fascinating world of restoration. Here, the past is not just remembered—it’s lovingly restored for generations to come.